
Is it even possible to stumble through your day without talk of “Climate Change”? In today’s world, especially with political campaigns brewing, climate change is a HOT topic.
What the political campaigns and news don’t talk about is the influence soil plays on climate change. According to Eric Brevik, Professor at Dickinson State University in North Dakota, “The organic matter in soil holds large amounts of carbon, which is also an important part of greenhouse gasses, including carbon dioxide.”
In fact, roughly 10% of the world’s carbon dioxide emissions are stored in the soil.
According to Rattan Lal, Director of Ohio State University’s carbon management and sequestration center, 800 Billion tons of carbon is in the atmosphere, 560 Billion tons in plants and animals, 25 Billion tons of carbon is stored in the soil.
In the past, there was a larger supply of carbon stored in the soil, but due to the agricultural practice of tilling (no longer a popular practice) and construction, as the soil is churned, carbon is released into the atmosphere. Today, we are still seeing the effects of tilling and construction remains prevalent.
Restoring Earth’s degraded soils could result in an increased ability to store carbon in the soil.
Carbon is added to the soil in three key ways.
1. Through photosynthesis
As fossil fuels are burned, carbon dioxide and other gases are released into the atmosphere and trap the sun’s energy.
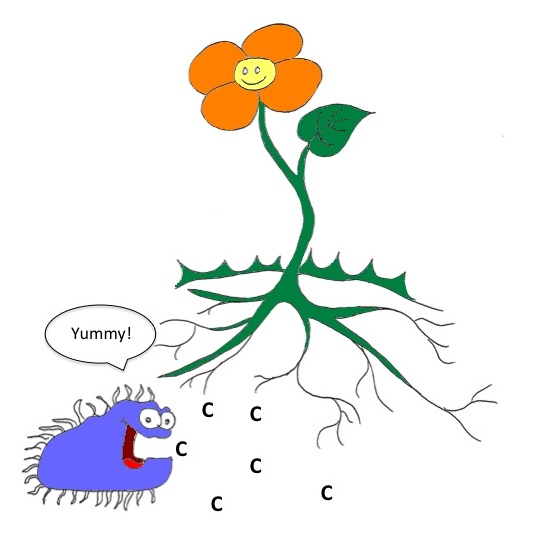
However, through photosynthesis, plants and some organisms capture the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it to carbon in a process called carbon fixation. The oxygen particles are released into the atmosphere while the carbon is utilized to produce sugars that are used as energy sources for the plant and help store food.
Luckily, plants over produce sugars and excrete 20 to 40% of their sugar to the soil. Within the soil, sugar acts as a food source for soil microorganisms that in turn, go to work protecting and nurturing the plant.
2. Animals exhale CO2 and decay
Critters within the soil breathe oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide, adding it to the soil atmosphere. At the same time, when organisms die, they decay and are turned into carbon rich organic matter.
Organic matter is full of nutrients and food sources for soil microorganisms, contributing to a healthy soil food web and thereby a healthy plant.
The soil food web is a system that cycles carbon through the soil life forms, constantly moving it from one life form to another. Keeping it trapped within the soil.
3. Leaves are full of carbohydrates
Leaves are full of carbohydrates. So, when they fall and decay, they are also adding carbon rich organic matter to the soil. Instead of bagging and throwing away your leaves and clippings (And risk them being burned in an incinerator which releases the carbon into the atmosphere), allow them to decay. Not only is it better for the environment, but it is also better for the plants and soil.
How to increase the soil’s Carbon holding capacity
According to Rattan Lal, plants with mycorrhizae can transform 15% more carbon than plants without mycorrhizae. Mycorrhizae fungi form a synergistic relationship with the plant, holding on to the carbon dioxide that plants exude into the soil.
In addition to utilizing products containing mycorrhizae, utilizing products or practices that maintains or strengthens the soil structure will also increase the soil’s ability to hold carbon.
 |
May 18, 2016
|
12:49 PM
|
May 18, 2016
|
12:49 PM

-2.jpg)
.jpg)
-4.jpg)
-2.jpg)
-1.jpg)
.webp)
-1%20(1).webp)
-831535-2.webp)




-2.jpg)
.jpg)
-4.jpg)
-2.jpg)
-1.jpg)
.webp)
-1%20(1).webp)
-831535-2.webp)








.jpg)