.png?width=700&name=blog%20header%20(28).png)
Farmers are beginning to look into carbon farming as a method to increase farm profitability, improve soil quality, and to help combat climate change.
Carbon farming includes a set of agricultural practices that, according to a recent MIT article are designed to “increase storage of atmospheric carbon in the soil. Many of these practices are common in organic farming, regenerative agriculture… and other approaches to food production.”
In addition to improving soil quality which could translate to improved yield, farmers could be paid carbon credits by private companies or government agencies to promote the practice, ultimately providing additional revenue to the farm.
According to an article by AgProfessional, “the global carbon market is estimated at $160 billion.”
A lot of work still needs to be done by both governments and private companies before carbon farming credits can become widespread, but there are instances where farmers are getting paid for carbon farming practices today. Countries like Australia already have a system in place for farmers. In the U.S., California has “started providing small grants from the state’s carbon cap-and-trade fund to farmers who employ techniques that promise to store more carbon.”
How does carbon farming work?
In a process known as carbon sequestration, crops photosynthesize, removing CO2 from the atmosphere and storing it. When they die, carbon continues to be stored in the soil or is released back into the atmosphere.
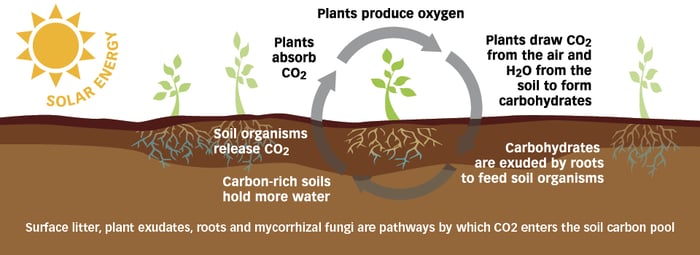
Infographic above by the Community Environmental Council
Certain farming practices can promote an increased ability for the land to store carbon. These practices include but are not limited to:
- No or low-till
- Leaving leftover biomass on the soil after harvest
- Using cover crops
- Crop rotation
- Integrated pest management practices
- Adding organic matter
Carbon Farming Sustainability Benefits
According to a study by The National Academy of Sciences, “global farmland could capture and store as much as 3 billion tons of additional carbon dioxide if farmers adopted a number of improved practices, including adding organic matter like manure or compost, shifting cultivation to favor crops that contribute more of their carbon to the soil, or using offseason to plant cover crops.”
But, there is still a lot we don’t know about the extent of carbon farming and how it benefits sustainability efforts to mitigate climate change. According to Noah Deich, Executive Director of Carbon180 at a panelist session on carbon farming at an annual Breakthrough Institute conference, “There are still a lot of unknowns about how soil microbe ecosystems actually work and what practices are most effective at capturing and storing carbon dioxide.”
Plus, cautions Princeton Researcher, Tim Searchinger, who studied carbon farming for a World Resources Institute report, there may be limits on what farmers can do to change their soil management practices. And, we still don’t know how much more carbon farmers can store in soil that is continually farmed.
“While there is a lot we still don’t know about carbon farming,” states David Stark, Ph.D. and President of Holganix Agriculture, “we do know that incorporating carbon farming practices improves soil health which can improve crop yield and farm profitability. We also know that carbon farming practices can promote a farm’s sustainability practices.”
It will be exciting to see how carbon farming opportunities offered by government and private companies through carbon credits, and continued research into carbon farming can help America’s farmers increase soil health and farm profitability.
Using Microbials To Improve Soil Health
Holganix Bio 800+ Agriculture charges soil with over 800 species of soil microbes to improve plant performance. What does that mean for you?
That means you build soil and root health, adding the benefits of better soil structure to whatever soil type you have. This translates to improved yield on crops, better playability on golf courses, and a reduced need for fertilizers and pesticides on lawns.
Learn more about the science behind Holganix Bio 800+ Agriculture below.
 |
September 17, 2020
|
4:50 PM
|
September 17, 2020
|
4:50 PM

-2.jpg)
.jpg)
-4.jpg)
-2.jpg)
-1.jpg)
.webp)
-1%20(1).webp)
-831535-2.webp)




-2.jpg)
.jpg)
-4.jpg)
-2.jpg)
-1.jpg)
.webp)
-1%20(1).webp)
-831535-2.webp)





.png?width=700&name=blog%20header%20(28).png)


.jpg)


